Is your child constantly tired despite getting enough sleep? Do they struggle with unexplained weight gain even though they’re active? As a parent, you’ve probably noticed these changes but weren’t sure what they meant. These could be early signs of insulin resistance in children – a condition that’s becoming increasingly common yet often goes unrecognized until it’s advanced.
When parents hear “insulin resistance,” they often think it’s an adult-only condition. However, this metabolic disorder is silently affecting more young lives than ever before. The most troubling part? The symptoms can be subtle, making early detection challenging for even the most attentive parents.
At IFitCenter, we’re dedicated to helping families understand and address childhood insulin resistance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything from early warning signs to practical management strategies, empowering you with the knowledge to protect your child’s metabolic health.
Early-Onset Insulin Resistance in Children
Picture your child’s cells as having tiny locks on their surfaces. Insulin acts like a special key that opens these locks, allowing sugar from food to enter the cells and provide energy. In insulin resistance, these locks begin to malfunction – it’s as if they’re becoming rusty, making it harder for the key to work properly.
Think of your child’s body like a busy city. When everything works properly, insulin (the traffic controller) efficiently directs sugar (the vehicles) to where it needs to go. But when insulin resistance develops, this traffic system starts to break down. More and more traffic controllers (insulin) are needed, but the traffic still doesn’t flow smoothly.
On the IFitCenter blog, we have published a free content bank about insulin resistance that can have a significant impact for you in controlling and preventing this metabolic disease. For access, simply use the links below:
- insulin resistance definition
- insulin resistance symptoms
- insulin resistance test
- can insulin resistance be reversed?
- How Long Does It Take to Reverse Insulin Resistance?
How Children Are Different
Unlike adults, children’s bodies are still growing and developing. This means insulin resistance can affect them differently. Their bodies are like buildings under construction – any disruption to the building process can have long-lasting effects on the final structure.
“Early-onset insulin resistance is particularly concerning because it occurs during critical developmental periods, potentially affecting growth, puberty, and long-term metabolic health,” explains a recent study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Age Matters: Children vs. Teens
In children (pre-teens), insulin resistance often develops quietly, potentially affecting their growth and development. For teenagers, hormonal changes during puberty naturally cause some insulin resistance, but this usually resolves after puberty – unless other risk factors are present.
Common Misconceptions aboun Insulin Resistance in Teens and Children
- Myth: Only overweight children develop insulin resistance
Reality: Children of any weight can develop this condition - Myth: Kids will “grow out of it”
Reality: Without proper management, it often progresses - Myth: It only affects blood sugar
Reality: It impacts overall growth, development, and health
Impact on Health and Development
Early insulin resistance can affect your child’s health in several ways. It’s like a domino effect – when one aspect of metabolism is disrupted, it can trigger a chain reaction affecting energy levels, growth patterns, and even mood and concentration at school.
Warning Signs of Signs of Insulin Resistance in Kids
Early detection of insulin resistance can significantly impact your child’s health outcomes. Understanding the warning signs specific to different age groups helps parents take timely action.
Child Insulin Resistance Symptoms
Before puberty, insulin resistance often shows subtle signs that parents might mistake for normal childhood changes. Recognizing these early indicators is crucial for prevention.
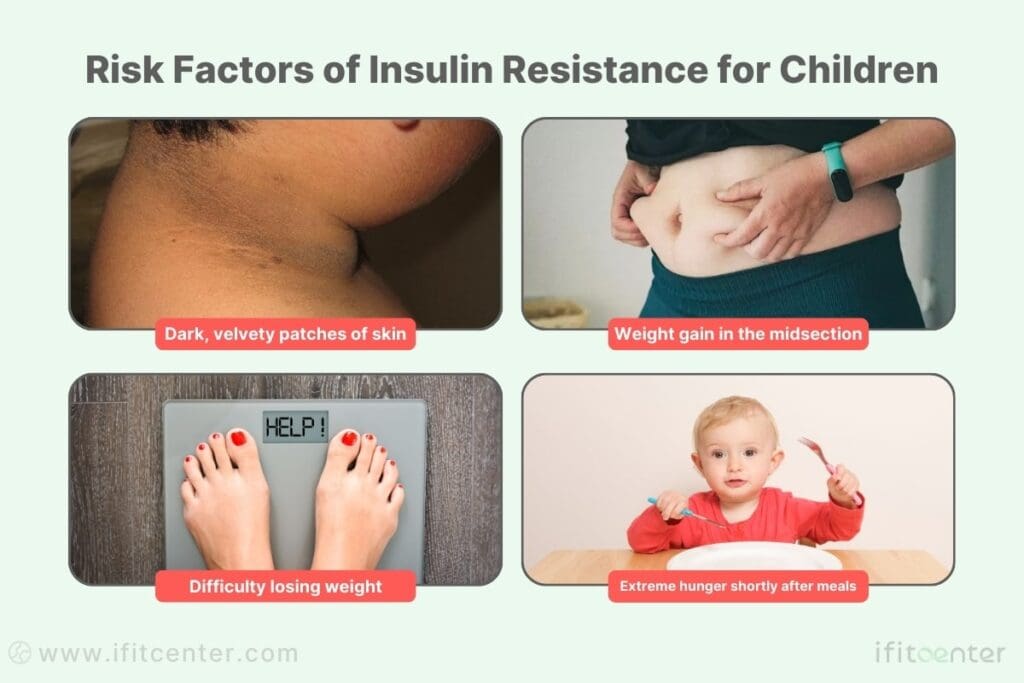
- Physical Changes of Insulin Resistance in Children
- Dark, velvety patches of skin (especially around the neck and armpits)
- Unexplained weight gain, particularly around the midsection
- Difficulty losing weight despite healthy eating
- Extreme hunger shortly after meals

- Behavioral Indicators of Insulin Resistance in Children
- Increased fatigue and low energy levels
- Difficulty concentrating in school
- Mood swings related to blood sugar fluctuations
- Changes in sleep patterns
Risk Factors of Insulin Resistance in Kids
Certain factors can increase your child’s likelihood of developing insulin resistance:
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Limited physical activity
- Poor sleep habits
- Excessive screen time
- Certain medications
Teen-Specific Warning Signs of Insulin Resistance

Adolescence brings unique challenges in identifying insulin resistance, as some signs may be masked by normal puberty changes.
- Physical Indicators
- Irregular menstrual cycles in girls
- Excessive facial or body hair growth
- Persistent acne resistant to treatment
- Changes in muscle development
“Adolescent insulin resistance often manifests differently from adults, making it crucial for parents and healthcare providers to understand these age-specific variations,” notes a recent study in the Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology.
Gender-Specific Considerations
Boys and girls may show different signs of insulin resistance during puberty:
Girls
- Irregular periods
- Polycystic ovary symptoms
- Weight gain around hips
Boys
- Delayed puberty signs
- Changes in muscle development
- Central weight gain
A Science-Backed Approach to Reversing Childhood Insulin Resistance
Children experiencing insulin resistance require more than just lifestyle advice—they need expert medical guidance tailored to their growing bodies. At IFitCenter, we provide a comprehensive health assessment and develop a customized weight management plan focused on restoring insulin sensitivity, promoting healthy weight loss, and ensuring long-term metabolic stability. Our structured, family-inclusive program empowers both children and parents to make informed health choices for a stronger, healthier future.
Let’s work together to support your child’s metabolic health. Book a professional evaluation with Dr. Babak today.
Testing and Treatment: Taking Action Against Insulin Resistance
Early intervention in childhood insulin resistance can significantly improve outcomes. Understanding the testing process and treatment options helps families make informed decisions about their child’s health.
Diagnostic Testing for Insulin Resistance
Several screening methods help identify insulin resistance in young people. These tests provide different pieces of the metabolic puzzle:
- Fasting Blood Tests
- Glucose levels
- Insulin levels
- Lipid profile
- Physical Assessments
- Body composition analysis
- Waist circumference measurements
- Blood pressure monitoring
“Understanding test results in children requires different reference ranges than adults, as normal values vary significantly during growth and development,” explains recent findings in Pediatric Diabetes.
To access the second part of the insulin resistance content, I invite you to use the links below:
Natural Treatment Approaches
Lifestyle modifications form the foundation of treating insulin resistance in young people. These changes should involve the whole family for the best results.
Evidence-Based Nutrition Guidelines
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods
- Include protein with every meal
- Choose fiber-rich vegetables and fruits
- Limit refined sugars and processed carbohydrates
- Maintain regular meal times
Age-Appropriate Physical Activity
Exercise recommendations vary by age and should be enjoyable to encourage long-term adherence:
Children (6-12 years)
- 60 minutes daily active play
- Variety of activities
- Focus on fun and movement
Teenagers (13-18 years)
- Structured exercise options
- Sports participation
- Resistance training
Sleep and Stress Management
Quality sleep and stress reduction play crucial roles in managing insulin resistance:
- Sleep Requirements
- Children: 9-11 hours nightly
- Teens: 8-10 hours nightly
- Consistent sleep schedule
- Stress Management
- Regular physical activity
- Mindfulness practices
- Family support systems
Family-Based Approach
Success in managing insulin resistance increases significantly when the whole family participates in lifestyle changes:
- Family meals together
- Group physical activities
- Shared health goals
- Supportive environment
Expert Care for Young People with Insulin Resistance
Managing insulin resistance in young people requires a personalized approach that considers each child’s unique needs. At IFitCenter, Dr. Babak Jamalian brings over 25 years of experience in helping children and teenagers improve their metabolic health through comprehensive care.
Our Comprehensive Treatment Approach
Dr. Babak and the IFitCenter team focus on creating individualized treatment plans that address all aspects of metabolic health:
- Initial Health Assessment
- Complete body composition analysis
- Detailed metabolic profile
- Family lifestyle evaluation
- Personalized goal setting
- Customized Treatment Plans
- Age-appropriate nutrition guidance
- Structured physical activity programs
- Regular progress monitoring
- Family support strategies
Supporting Your Child’s Journey
Our treatment program includes:
- Regular check-ups with Dr. Babak
- Body composition tracking
- Nutritional counseling sessions
- Family education workshops
- Ongoing lifestyle support
Success Through Family Support
At IFitCenter, we believe in empowering families with the knowledge and tools they need. Our approach includes:
- Family nutrition planning
- Group activity suggestions
- Regular progress updates
- Practical lifestyle tips
- Ongoing support and guidance
Take the first step in supporting your child’s metabolic health. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Babak at IFitCenter to discuss your child’s specific needs and create a personalized treatment plan.
Your Next Steps in Managing Insulin Resistance in Children
Understanding and managing insulin resistance in young people requires attention and consistent effort. Let’s recap the essential points and outline practical steps for moving forward.
Key Takeaways
- Early Detection Matters
- Watch for physical changes like skin darkening
- Monitor energy levels and hunger patterns
- Pay attention to unexplained weight changes
- Age-Specific Considerations
- Different symptoms in children vs. teens
- Hormonal influences during puberty
- Growth-related factors
- Lifestyle Changes
- Focus on whole-food nutrition
- Regular physical activity
- Adequate sleep and stress management
Action Plan for Parents
Immediate Steps
- Schedule a comprehensive health assessment
- Begin monitoring your child’s symptoms
- Start implementing dietary improvements
- Create an activity schedule
- Establish consistent sleep routines
Weekly Goals
- Plan healthy family meals
- Schedule family physical activities
- Monitor progress and symptoms
- Maintain regular sleep schedule
- Track lifestyle changes
Monthly Objectives
- Review progress with healthcare provider
- Adjust strategies as needed
- Celebrate improvements
- Set new health goals
Additional Resources
- Pediatric metabolic health guidelines
- Family-friendly recipe collections
- Physical activity guides
- Sleep hygiene tips
- Support group information
“The key to managing insulin resistance in young people is consistent, family-wide commitment to healthy lifestyle changes. Every small step counts toward better metabolic health.”
To access other content on the IFitCenter’s blog, you can use the following links:
References for Insulin Resistance in Kids
- Gao F, Wang G, Wang L, et al. An update of the consensus statement on insulin resistance in children and adolescents. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2022;13:1061524. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1061524
- Mastroianni Kirsztajn G, Janurkar B, Monteiro de Barros V, et al. Insulin Resistance in Children. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2019;10:342. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00342
- Chowdhury S, Akhtar S, Rahman M, et al. Identification of cutoff value for Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) in Children. medRxiv. 2025. DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.05.25320014
- Gong Q, et al. Global trends in type 1 diabetes in adolescents and young adults from 1990 to 2019: An age-period-cohort analysis. Nature. 2024;9(1):1-10. DOI: 10.1038/s41390-024-03554-0
- Paulmichl K, et al. Modified Single Point Insulin Sensitivity Estimator for Assessment of Insulin Sensitivity in Pediatric Obesity. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2024;15:1439901. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1439901



