Think having normal blood sugar means you’re safe from diabetes? This common belief could be putting your health at risk. Groundbreaking research published in Cell Metabolism reveals a startling truth: the connection between insulin resistance and diabetes begins up to 13 years before diagnosis – long before blood sugar levels rise above normal.
Many believe type 2 diabetes strikes suddenly, but science tells a different story. Like a slow-burning fuse, insulin resistance quietly progresses for years, setting the stage for diabetes while blood sugar readings remain deceptively normal. At IFitCenter, we’ll explore this critical connection, helping you understand the early warning signs that most people miss.
Imagine discovering a small leak in your roof. Fix it early, and you prevent major damage. Similarly, understanding how insulin resistance leads to diabetes gives you the power to act before significant health problems develop. Let’s uncover the science behind this vital connection and learn what you can do about it today.
The Science Behind Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
Imagine your body’s cells have tiny doors, and insulin is the key that opens these doors to let sugar in from your bloodstream. In a healthy person, this system works smoothly – insulin opens the doors, sugar enters the cells, and blood sugar levels stay balanced. But what happens when this system starts to fail?
Think of insulin resistance like a rusty lock. Even though you have the right key (insulin), it becomes harder and harder to open the door. Your body responds by making more and more keys (producing more insulin), trying desperately to get those doors open. For a while, this works – your blood sugar stays normal because your body is working overtime producing extra insulin.
“A common misconception is that only overweight individuals develop insulin resistance. In reality, I regularly see metabolically unhealthy patients with normal weight who show signs of insulin resistance. Body weight alone doesn’t tell the full story – it’s the distribution of fat, particularly around internal organs, that signals metabolic health.”
Dr. Babak Jamalian, Family Physician.
The Three Stages of Progression
Recent research has identified three distinct stages in the progression from insulin resistance to type 2 diabetes:
- Early Stage: Your body produces extra insulin to maintain normal blood sugar. You might feel fine, but your insulin levels are rising.
- Middle Stage: Your cells become increasingly resistant, requiring even more insulin. Blood sugar may start to creep up, but still appears “normal” on standard tests.
- Late Stage: Your pancreas can’t keep up with the demand for insulin. Blood sugar begins to rise significantly, leading to diabetes diagnosis.
Key Metabolic Changes
During this progression, several critical changes occur in your body:
- Your pancreas works harder than normal, producing up to 5 times more insulin
- Fat storage increases, especially around internal organs
- Inflammation levels rise throughout the body
- Energy levels may decrease as cells struggle to access glucose
Understanding these changes is crucial because they happen long before traditional diabetes tests show any problems. This is why measuring insulin levels, not just blood sugar, can provide earlier warning signs of developing diabetes.
Insulin resistance is a metabolic disease with very high prevalence. The good news is that by understanding this problem, you can easily control it or prevent it from occurring.
On the IFitCenter blog, we have provided you with a completely free content repository about insulin resistance based on a physician’s experiences as well as the latest scientific research conducted. To access the first part of the materials, you can use the links below:
- understanding insulin resistance
- insulin resistance test
- insulin resistance in children
- how to reverse insulin resistance
- How Long Does Insulin Resistance Treatment Take?
Early Warning Signs: From Insulin Resistance to Type 2 Diabetes
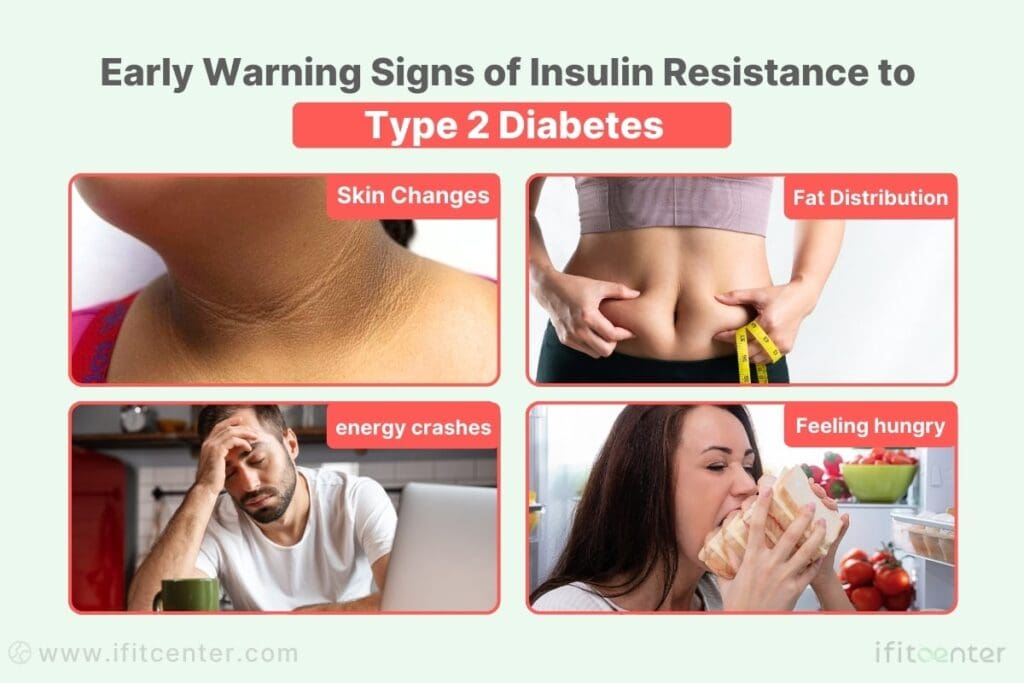
Most people don’t realize they have insulin resistance until it progresses to diabetes. However, your body sends subtle signals long before blood sugar levels rise. Understanding these early warning signs could be your key to preventing type 2 diabetes.
Physical Signs of Insulin Resistance
Your body has several ways of showing insulin resistance before it appears on standard blood tests:
- Skin Changes: Dark patches around your neck or armpits (acanthosis nigricans)
- Fat Distribution: Increasing waist size, especially compared to hip measurement
- Energy Patterns: Fatigue after meals or afternoon energy crashes
- Hunger Changes: Feeling hungry soon after eating or constant cravings
Hidden Biomarkers in Your Blood Work
Standard blood sugar tests often miss early insulin resistance. Here are the key biomarkers that can reveal problems early:
- Fasting Insulin: The earliest indicator – can be elevated years before blood sugar rises
- Triglycerides: Levels above 150 mg/dL may signal insulin resistance
- HDL Cholesterol: Lower levels often accompany insulin resistance
- Hemoglobin A1C: Important to track trends even within “normal” range
“Fasting insulin levels can reveal metabolic problems up to a decade before traditional diabetes tests show any issues.”
Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2023
Progression Timeline
The development of type 2 diabetes from insulin resistance typically follows this pattern:
- Early Phase (2-5 years):
- Rising insulin levels
- Normal blood sugar
- Subtle energy changes
- Middle Phase (5-10 years):
- Higher insulin production
- Blood sugar at upper normal range
- More noticeable symptoms
- Late Phase (10+ years):
- Very high insulin levels
- Rising blood sugar
- Clear physical symptoms
When to Seek Professional Help
Consider professional evaluation if you notice:
- Two or more physical warning signs
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Unexplained weight changes
- Persistent fatigue after meals
- Blood work showing borderline results
Early intervention is crucial – waiting until blood sugar rises significantly means missing valuable prevention opportunities. Regular monitoring of these indicators, especially fasting insulin levels, can help catch insulin resistance before it progresses to diabetes.
Can Insulin Resistance Lead to Diabetes?
While insulin resistance can affect anyone, certain factors significantly increase your risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes. Understanding these risk factors helps you take appropriate preventive actions.
Genetic Risk Factors
Your genetic makeup plays a crucial role in determining insulin resistance risk:
- Family History: Having a first-degree relative with type 2 diabetes doubles your risk
- Ethnic Background: Higher risk in South Asian, Middle Eastern, and African populations
- Age: Risk increases after age 45, though younger people are increasingly affected
- Gender-Specific Factors: Women with PCOS face increased risk due to hormonal influences
Lifestyle Risk Factors
Daily choices significantly impact your progression from insulin resistance to diabetes:
- Dietary Patterns:
- High intake of processed carbohydrates
- Frequent consumption of sugary beverages
- Irregular eating patterns
- Large portion sizes
- Physical Activity:
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Prolonged sitting
- Lack of regular exercise
- Sleep Patterns:
- Less than 6 hours or more than 9 hours of sleep
- Poor sleep quality
- Shift work disrupting natural sleep cycles
Environmental Risk Factors
Your environment can significantly influence insulin resistance:
- Stress Exposure: Chronic stress increases cortisol, affecting insulin sensitivity
- Environmental Toxins: Certain chemicals can disrupt metabolic processes
- Urban Living: Less access to outdoor activities and healthy food options
- Work Environment: Long sitting hours and limited movement opportunities
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Several health conditions can accelerate the progression from insulin resistance to diabetes:
- Metabolic Conditions:
- High blood pressure
- Elevated cholesterol levels
- Fatty liver disease
- Hormonal Disorders:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Thyroid conditions
- Cushing’s syndrome
Understanding your personal risk factors is crucial for prevention. While some factors like genetics cannot be changed, many can be modified through lifestyle changes.
Preventing the Progression to Type 2 Diabetes
Research shows that up to 70% of people with insulin resistance can prevent or significantly delay the development of type 2 diabetes through evidence-based lifestyle changes. Let’s explore the scientifically proven strategies that can help reverse insulin resistance.
To view the second part of content related to insulin resistance, I invite you to use the links below:
- supplements for insulin resistance
- best foods for insulin resistance
- insulin resistance symptoms
- insulin resistance weight gain
- Is Fasting Good for Insulin Resistance?
Science-Backed Dietary Approaches
Recent clinical studies have identified specific dietary patterns that improve insulin sensitivity:
- Meal Timing:
- Allow 12-14 hours between dinner and breakfast
- Eat main meals earlier in the day
- Avoid late-night eating
- Food Choices:
- Prioritize protein with each meal
- Include fiber-rich vegetables
- Choose whole foods over processed options
- Limit refined carbohydrates
Evidence-Based Exercise Strategies
Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity through multiple mechanisms:
- Daily Movement:
- Break up sitting time every 30 minutes
- Aim for 7,000-10,000 steps daily
- Include regular walking after meals
- Structured Exercise:
- 2-3 resistance training sessions weekly
- 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity
- Mix of high and low-intensity activities
“Most people believe exercise needs to be intense to improve insulin sensitivity. However, something as simple as a short walk after meals can have a profound effect on how your body processes glucose. This post-meal movement helps your muscles use glucose without requiring additional insulin – a simple yet powerful strategy for maintaining metabolic health.”
Dr. Babak Jamalian, Family Physician.
Sleep and Stress Management
Research reveals that sleep and stress significantly impact insulin sensitivity:
- Sleep Optimization:
- Maintain consistent sleep schedule
- Aim for 7-8 hours nightly
- Create a dark, cool sleeping environment
- Avoid screens before bedtime
- Stress Reduction:
- Practice regular mindfulness or meditation
- Incorporate daily relaxation techniques
- Maintain social connections
- Consider stress-management counseling
Remember that small changes, when consistently maintained, can lead to significant improvements in insulin sensitivity. The key is choosing sustainable modifications that you can maintain long-term.
Reversing Insulin Resistance Before It Becomes Diabetes
Insulin resistance is not just a warning sign—it is the silent precursor to type 2 diabetes. Addressing it before blood sugar levels rise is critical in preventing long-term complications. At IFitCenter, we take a proactive, medically supervised approach to reversing insulin resistance and optimizing metabolic health.
Under the leadership of Dr. Babak Jamalian, our clinical team specializes in:
✔ Comprehensive metabolic assessments to detect insulin resistance early
✔ Structured, science-backed weight management programs to restore insulin sensitivity
✔ Personalized lifestyle interventions designed for long-term metabolic stability
If you are experiencing symptoms of insulin resistance or have risk factors for diabetes, now is the time to take action. Early intervention can prevent irreversible metabolic damage.
Professional Monitoring and Management
Effective management of insulin resistance requires regular monitoring of specific health markers. Understanding these measurements helps you track progress and make timely interventions before progression to type 2 diabetes.
Essential Health Markers to Monitor
Several key measurements provide crucial insights into insulin resistance progression:
- Primary Markers:
- Fasting insulin levels
- Fasting blood glucose
- Hemoglobin A1C
- HOMA-IR score (insulin resistance index)
- Supporting Indicators:
- Triglyceride levels
- HDL cholesterol
- Blood pressure readings
- Waist circumference measurements
Recommended Testing Frequency
Research-based monitoring schedule for optimal prevention:
- Every 3-4 Months:
- Fasting insulin and glucose levels
- Body composition measurements
- Blood pressure checks
- Every 6 Months:
- Complete lipid panel
- Hemoglobin A1C
- Comprehensive metabolic panel
- Annually:
- Full medical review
- Cardiovascular risk assessment
- Comprehensive health screening
Warning Signs Requiring Medical Attention
Seek professional evaluation if you notice:
- Consistent fasting glucose above 100 mg/dL
- Unexplained weight changes
- Frequent fatigue or energy crashes
- New or worsening skin changes
- Irregular blood pressure readings
“Regular monitoring of insulin levels, not just blood sugar, provides the earliest opportunity for intervention in preventing type 2 diabetes.”Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2023
Professional Management Strategies
Effective management often requires a combination of:
- Regular health assessments
- Personalized lifestyle recommendations
- Ongoing progress monitoring
- Adjustment of interventions based on results
Understanding your personal health markers and their implications can be complex. Professional guidance can help interpret these measurements and create a personalized monitoring plan. Schedule a consultation to discuss your specific needs and concerns.
A Comprehensive Approach to Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Preventing the progression from insulin resistance to type 2 diabetes requires a structured, personalized approach. At IFitCenter, we’ve developed a comprehensive program that addresses every aspect of metabolic health under the expert guidance of Dr. Babak Jamalian, a family physician specialist with over 31 years of experience in metabolic health.
Our Three-Phase Prevention Program
- Initial Assessment Phase:
- Comprehensive 72-parameter blood analysis
- Advanced body composition measurement
- Detailed medical history review
- Personal consultation with Dr. Babak
- Customized Intervention Phase:
- Personalized nutrition protocol
- Lifestyle modification guidance
- Regular body composition monitoring
- Bi-weekly progress evaluations
- Long-term Maintenance Phase:
- Ongoing progress tracking
- Protocol adjustments as needed
- Sustainable lifestyle education
- Continuous support system
Professional Support System
Our program provides comprehensive support throughout your journey:
- Medical Supervision:
- Regular consultations with Dr. Babak
- Ongoing health marker monitoring
- Personalized protocol adjustments
- Lifestyle Support:
- Practical nutrition guidance
- Exercise recommendations
- Stress management techniques
Our Success Indicators
The effectiveness of our approach is reflected in our client outcomes:
- Improved insulin sensitivity in over 80% of clients
- Significant improvements in body composition
- Enhanced energy levels and overall well-being
- Long-term maintenance of results
Dr. Babak’s Expertise
As our Medical Director, Dr. Babak Jamalian brings extensive experience in managing metabolic conditions. His approach combines the latest medical knowledge with practical, sustainable solutions for each individual’s needs. Dr. Babak personally oversees each client’s progress, ensuring optimal results through regular monitoring and protocol adjustments.
Take the first step toward preventing type 2 diabetes. Schedule your complimentary consultation with Dr. Babak to receive a personalized assessment and learn how our comprehensive program can help you achieve optimal metabolic health. Contact us.
Understanding and Acting on the Insulin Resistance-Diabetes Connection
The relationship between insulin resistance and diabetes represents a crucial window of opportunity. Understanding this connection empowers you to take control of your metabolic health before diabetes develops.
Key Takeaways
- Early Recognition: Insulin resistance often develops years before blood sugar rises
- Warning Signs: Changes in energy, body composition, and skin can signal insulin resistance
- Prevention Power: Early intervention can prevent or significantly delay type 2 diabetes
- Professional Support: Medical supervision significantly improves prevention success rates
Your Action Plan
Take these steps to protect your metabolic health:
- Immediate Actions:
- Schedule a comprehensive health assessment
- Begin monitoring key health markers
- Implement basic lifestyle changes
- Short-term Goals:
- Optimize meal timing and choices
- Establish regular physical activity
- Improve sleep patterns
- Long-term Strategy:
- Regular professional monitoring
- Ongoing lifestyle adjustments
- Continuous education
Additional Resources
Expand your understanding with these reliable sources:
- International Diabetes Federation Guidelines
- American Diabetes Association Prevention Resources
- World Health Organization Diabetes Prevention Guide
- Local diabetes prevention programs
Remember: The progression from insulin resistance to type 2 diabetes isn’t inevitable. With proper understanding, early intervention, and professional support, you can maintain optimal metabolic health. Take the first step today by assessing your risk factors and consulting with healthcare professionals who can guide your prevention journey.
To access other content on the IFitCenter’s blog, you can use the following links:
References for Diabetes vs Insulin Resistance
This article is based on current scientific research and evidence from the following peer-reviewed sources:
- Wang L, et al. Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 2022;7(1):92. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01073-0
- Zhang Y, et al. The crucial role and mechanism of insulin resistance in metabolic diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1149239. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1149239
- Abdullah I. Aedh, et al. A Glimpse into Milestones of Insulin Resistance and an Updated Review of Its Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2023;15(4):921. DOI: 10.3390/nu15040921
- Thompson KH, et al. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity. 2020;13:3611–3626. DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S275898
- StatPearls Publishing. Insulin Resistance – Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology, and Management Strategies. StatPearls. 2023; August Update.
- Kim YS, et al. Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies in Diabetes Management. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021;36(6):1125–1140. DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0280



