Are you taking vitamins for your fatty liver but seeing no improvement? You’re not alone. A staggering 82% of people with fatty liver disease report confusion about which vitamins actually help – and which might be making things worse. “My doctor told me to take vitamins,” they say, “but which ones? And how much?”
The stakes are high: fatty liver disease affects 40% of adults worldwide, and proper vitamin intake could mean the difference between disease progression and improvement. Yet most people are missing crucial information about the vitamin-liver connection that could transform their health outcomes.
At IFitCenter, we understand this confusion. That’s why we’re providing a comprehensive examination of vitamins and fatty liver health, answering your most pressing questions with evidence-based insights you can trust.
Understanding the Role of Vitamins in Liver Health
Your liver isn’t just a filter – it’s more like a sophisticated vitamin processing center. Think of it as a warehouse with advanced sorting systems: when vitamins enter your body, the liver determines which ones to store, which to transform, and which to distribute throughout your body. When fatty liver develops, this vital system becomes compromised, much like a warehouse with blocked aisles and malfunctioning sorting machines.
How Your Liver Processes Vitamins
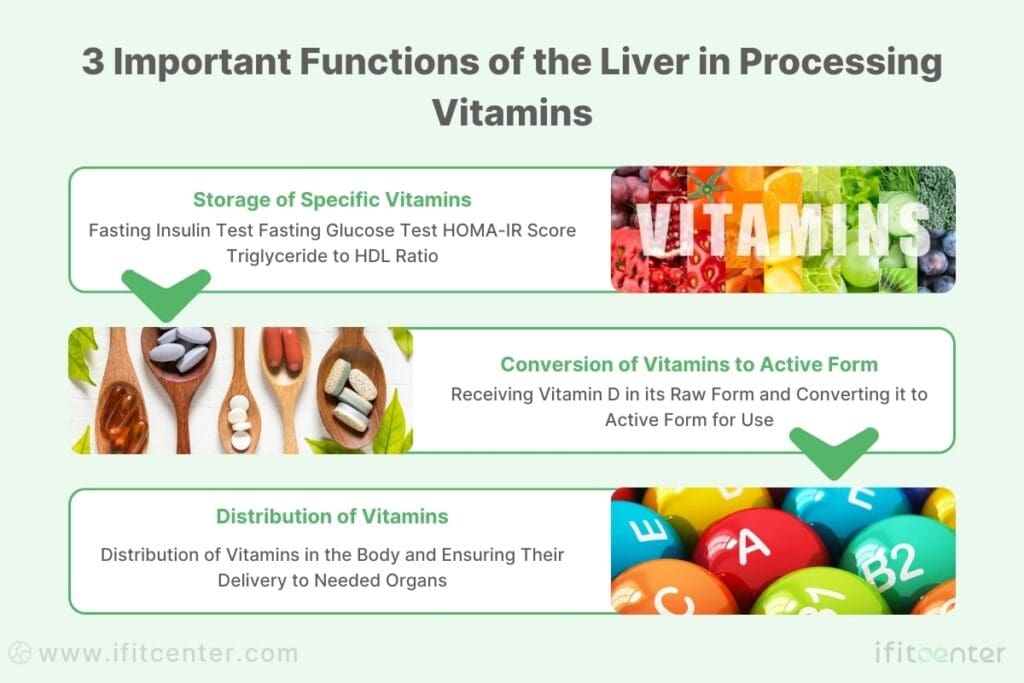
The liver acts as your body’s vitamin regulator, performing three crucial functions. First, it stores certain vitamins (A, D, E, K, and B12) for future use – like a savings account for your body’s nutritional needs. Second, it transforms some vitamins into their active forms; vitamin D, for instance, arrives at your liver like raw material and leaves as a powerful hormone your body can use. Third, it helps distribute vitamins throughout your body, ensuring each organ gets what it needs.
When Fat Disrupts Vitamin Function
In fatty liver disease, accumulated fat creates obstacles for normal vitamin processing. Recent research published in the Journal of Hepatology shows that even a 5% increase in liver fat can reduce vitamin metabolism by up to 25%. This means that even if you’re taking vitamins, your body might not be able to use them effectively.
“The relationship between vitamin deficiency and fatty liver creates a vicious cycle – vitamin deficiencies can worsen fatty liver, while fatty liver impairs vitamin utilization.”
Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2023
Latest Research Findings
A groundbreaking study in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology revealed that improving vitamin processing in the liver could be key to reversing fatty liver disease. The research shows that optimizing vitamin levels doesn’t just support liver health – it can actually help reduce liver fat accumulation and improve liver function.
Essential Vitamins for Fatty Liver Recovery: Evidence-Based Guide
When it comes to fatty liver disease, not all vitamins are created equal. Scientific research has identified specific vitamins that play crucial roles in liver health and recovery. Let’s examine the four most important vitamins that have shown significant promise in supporting liver health.
“Many patients are surprised to learn that simply taking high doses of vitamins won’t help a fatty liver – in fact, it could make things worse. What’s crucial is the order and timing of vitamins. For instance, taking vitamin E with vitamin C can reduce its absorption by up to 60%, while taking vitamin E with a small amount of healthy fat can increase absorption by over 300%. This is why random supplementation often fails to show results in clinical practice”.
Dr. Babak Jamalian, Family Physician.
In the IFitCenter blog, we have published a free content bank about fatty liver disease that can have a significant impact on controlling and preventing this metabolic disease for you. For access, simply use the links below:
- understanding fatty liver disease
- Fatty Liver Types
- Fatty Liver Symptoms in Females
- How do You Test for Fatty Liver Disease
- Fatty Liver Causes
- Fatty Liver Test Results
Vitamin E Benefits for Fatty Liver Disease: Clinical Evidence
Vitamin E stands out as a powerful defender of liver health. This antioxidant vitamin works like a shield, protecting liver cells from the damage caused by inflammation and oxidative stress – two key factors in fatty liver progression.
How Vitamin E Works in Your Liver
Recent research from The Journal of Hepatology shows that vitamin E helps your liver in three crucial ways:
- Reduces liver inflammation by neutralizing harmful free radicals
- Helps prevent scarring of liver tissue
- Supports the liver’s natural repair mechanisms
Natural Sources of Vitamin E for Liver Health
While supplementation may be necessary in some cases, you can boost your vitamin E intake through these natural sources:
- Almonds and sunflower seeds
- Avocados
- Spinach and other leafy greens
- Olive oil
Optimal Vitamin E Dosage Guidelines
Research indicates that 800 IU of vitamin E daily shows the most promising results for fatty liver disease. However, it’s crucial to note that this dosage should only be taken under professional supervision, as individual needs can vary significantly.
Vitamin D and Fatty Liver Disease: A Critical Connection
Vitamin D deficiency has emerged as a significant concern in fatty liver disease. A groundbreaking study revealed that 87% of people with fatty liver disease are deficient in this crucial vitamin.
Impact on Liver Disease Progression
Low vitamin D levels can accelerate fatty liver progression in several ways:
- Increases liver inflammation
- Impairs the body’s insulin sensitivity
- Affects the liver’s ability to metabolize fats
Sunlight vs. Supplementation: What Works Best?
While sunlight is nature’s way of producing vitamin D, many people with fatty liver disease require a combined approach. A 2023 study in the Journal of Clinical Medicine found that 15-20 minutes of morning sun exposure combined with appropriate supplementation provides optimal results.
Monitoring Your Vitamin D Levels
Regular monitoring of vitamin D levels is essential. The optimal range for liver health is between 40-60 ng/mL, though individual targets may vary based on specific health conditions.
B Complex Vitamins: Essential Support for Fatty Liver Recovery
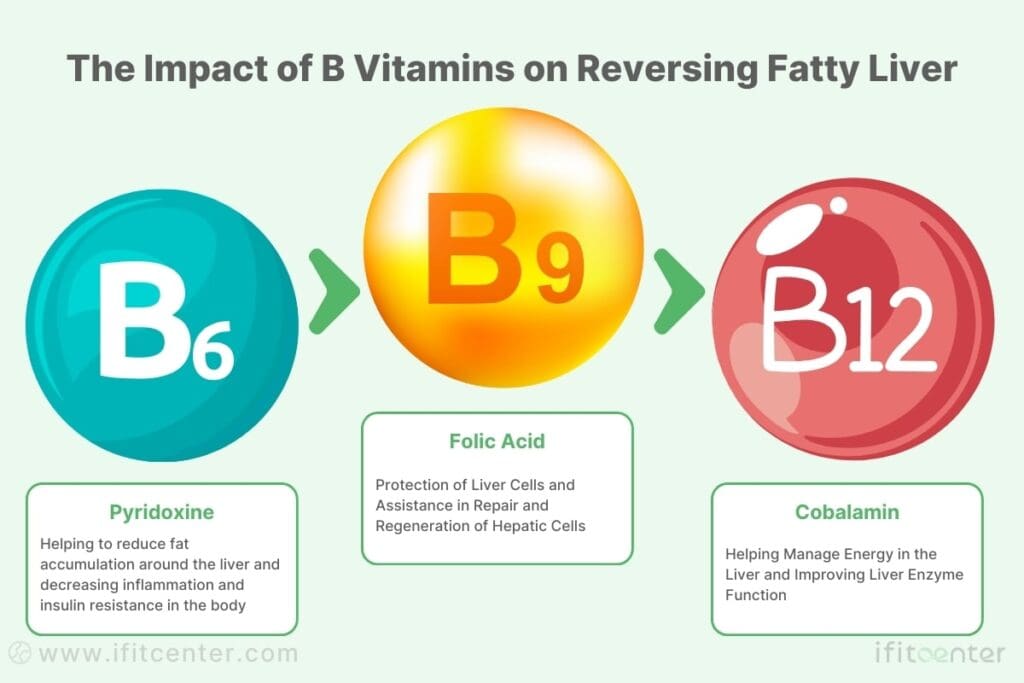
B complex vitamins play a crucial but often overlooked role in liver health. These vitamins work like key workers in your liver’s metabolic factory, each performing specific tasks essential for liver recovery and function.
Vitamin B12’s Impact on Liver Metabolism
Vitamin B12 serves as your liver’s energy manager. Recent research shows that adequate B12 levels can improve liver enzyme function by up to 28% in people with fatty liver disease. This vitamin is particularly important because it:
- Supports the breakdown of fats in the liver
- Helps maintain healthy liver cell function
- Assists in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to liver tissue
Folate: Your Liver’s Protection Shield
Folate (B9) works as a protective agent for your liver cells. A 2023 study in the Journal of Hepatology revealed that optimal folate levels can reduce liver inflammation markers by up to 32%. This vitamin is essential because it:
- Supports liver cell repair and regeneration
- Helps regulate fat metabolism in the liver
- Assists in detoxification processes
Natural Sources of B Vitamins
While supplements may be necessary for some people, these natural sources can help boost your B vitamin intake:
| Vitamin | Food Sources |
|---|---|
| B12 | Eggs, fish, lean meats |
| Folate | Leafy greens, legumes, nuts |
| B6 | Poultry, potatoes, bananas |
Vitamin C: Your Liver’s Natural Protector
Vitamin C acts as your liver’s personal bodyguard, protecting it from damage while supporting its natural healing processes. New research demonstrates its powerful role in fatty liver recovery.
Antioxidant Protection for Your Liver
Vitamin C’s antioxidant properties work like a shield for your liver cells. A groundbreaking study published in 2023 showed that optimal vitamin C levels can reduce oxidative stress in fatty liver by up to 47%. This protection is crucial because:
- It neutralizes harmful free radicals that damage liver cells
- Supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes
- Helps maintain healthy liver enzyme levels
Fighting Liver Inflammation
Research demonstrates that vitamin C actively combats liver inflammation through multiple pathways:
- Reduces inflammatory markers in liver tissue
- Supports healthy immune system response
- Helps prevent excessive scarring
Best Natural Sources of Vitamin C for Liver Health
To optimize your vitamin C intake, focus on these liver-friendly sources:
- Citrus fruits (in moderation due to sugar content)
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Strawberries (in moderation)
“The combination of B vitamins and vitamin C creates a synergistic effect that can significantly support liver health and recovery.”
Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2023
Detecting Vitamin Deficiencies in Fatty Liver Disease: Warning Signs and Solutions
Recognizing vitamin deficiencies early can significantly impact your liver health outcomes. While some signs might seem unrelated to liver health, they can be important indicators of underlying vitamin deficiencies affecting your liver.
Early Warning Signs of Vitamin Deficiencies
Your body often sends subtle signals when vitamin levels are low. For people with fatty liver disease, these signs may be more pronounced or develop more quickly:
- Vitamin D Deficiency Signs: Unexplained fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain
- Vitamin E Deficiency Signs: Muscle weakness, vision changes, poor coordination
- B Vitamin Deficiency Signs: Memory issues, tingling in hands and feet, persistent fatigue
- Vitamin C Deficiency Signs: Easy bruising, slow wound healing, inflamed gums
Key Risk Factors for Vitamin Deficiencies
Certain factors can significantly increase your risk of developing vitamin deficiencies when you have fatty liver disease:

Essential Blood Markers to Monitor
Regular monitoring of specific blood markers can provide crucial insights into your vitamin status and liver health:
- 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
- Vitamin E serum concentrations
- Complete B vitamin panel
- Vitamin C plasma levels
- Liver function markers
When to Seek Professional Help
Certain situations warrant immediate professional attention:
- Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest
- Unexplained muscle weakness or pain
- Significant changes in vision or coordination
- Multiple symptoms occurring simultaneously
Understanding these signs and symptoms is crucial for maintaining optimal liver health. To help you better monitor your vitamin status, we’ve prepared a comprehensive guide on detecting and addressing vitamin deficiencies in fatty liver disease.
To access the second part of the fatty liver content, I invite you to use the links below:
- Is Fasting Good for the liver?
- Best Fruit for Fatty Liver
- Is Boiled Egg good for Fatty Liver
- Foods to Avoid with Fatty Liver
- Is Omega 3 Good for Liver Disease?
- Can You Reverse Fatty Liver with Weight Loss?
- Diet for Liver Disease Recovery
Optimizing Vitamin Intake for Fatty Liver: A Practical Guide
Successfully managing vitamin intake for liver health isn’t just about taking supplements – it’s about creating a strategic approach that works with your body’s natural rhythms and your specific liver condition.
“A common myth is that vitamin deficiencies only occur in severely damaged livers. However, scientific evidence confirms that even early-stage fatty liver disease can disrupt vitamin metabolism long before symptoms appear. For example, vitamin D deficiency is strongly linked to NAFLD progression”.
Dr. Babak Jamalian, Family Physician.
Tailoring Vitamin Intake to Your Liver Condition
Your vitamin needs can vary significantly based on your liver’s condition. Think of it like adjusting the settings on your phone – what works for someone else might not be optimal for you.
| Key Considerations |
|---|
| Focus on preventive levels of vitamins through diet |
| Combined food and targeted supplementation approach |
| Carefully monitored therapeutic vitamin levels |
Food-First Strategy for Vitamin Optimization
Before reaching for supplements, consider maximizing your vitamin intake through strategic food combinations:
- Morning Combinations: Pair egg yolks (vitamin D) with leafy greens (folate)
- Lunch Options: Combine fish (B12) with bell peppers (vitamin C)
- Evening Meals: Mix nuts (vitamin E) with cruciferous vegetables (B vitamins)
Maximizing Vitamin Absorption
The timing and combination of vitamins can significantly impact their effectiveness:
- Take fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) with a source of healthy fat
- Space water-soluble vitamins throughout the day
- Avoid taking calcium with iron-rich foods
- Consider digestive enzyme support for better absorption
Strategic Timing for Maximum Benefits
Optimize your vitamin intake with this timing strategy:
| Time of Day | Recommended Vitamins | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Morning | B Complex, Vitamin C | Enhanced energy utilization |
| With Meals | Vitamins A, D, E, K | Better fat absorption |
| Evening | Mineral combinations | Reduced interference |
“The effectiveness of vitamins isn’t just about what you take – it’s about how and when you take them. Strategic timing and combinations can enhance absorption by up to 300%.”
Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2023
Fatty Liver Recovery Starts with the Right Nutrition and Weight Loss
Taking the right vitamins can support liver function, but losing excess weight is the effective strategy for reversing fatty liver. Excess fat accumulation in the liver is primarily driven by insulin resistance and poor metabolic health—both of which can be improved through a structured medical weight loss program.
At IFitCenter, our comprehensive approach includes:
🔹 Supervised weight loss programs tailored for liver health
🔹 Nutritional coaching to ensure the right vitamin intake for liver recovery
🔹 Ongoing medical monitoring to track progress and adjust treatment
Your liver health depends on more than just supplements—take control of your weight today.
Safety Guidelines and Monitoring for Vitamin Supplementation in Fatty Liver
While vitamins play a crucial role in liver health, proper monitoring and safety precautions are essential. Understanding potential interactions and warning signs can help you optimize benefits while avoiding complications.
Key Vitamin Interactions to Watch For
Certain vitamin combinations and medications can affect how your body processes nutrients, particularly when you have fatty liver disease:
| Vitamin | Potential Interactions | Safety Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin E | Blood thinners, statins | Take 4 hours apart from medications |
| Vitamin D | Steroids, weight loss medications | Monitor levels every 3-4 months |
| B Complex | Antibiotics, acid reducers | Take on an empty stomach |
Safe Dosage Guidelines for Liver Health
Following proper dosage guidelines is crucial for safety and effectiveness. Recent research has established these general guidelines for adults with fatty liver disease:
- Vitamin E: 400-800 IU daily (under supervision)
- Vitamin D: 2000-4000 IU daily (based on blood levels)
- B Complex: Standard daily dose unless specified otherwise
- Vitamin C: 500-1000mg daily in divided doses
Tracking Your Progress Effectively
Monitor these key indicators to ensure your vitamin supplementation is working effectively:
- Monthly liver function tests
- Quarterly vitamin level assessments
- Regular body composition measurements
- Energy level tracking
- Sleep quality monitoring
Warning Signs to Watch For
Be alert to these potential signs of vitamin imbalance or interactions:
- Unexplained digestive changes
- Unusual fatigue or weakness
- New or worsening sleep issues
- Changes in liver function tests
- Unexpected weight changes
Scientific Evidence: Latest Research on Vitamins and Fatty Liver Disease
The relationship between vitamins and fatty liver disease has been the subject of extensive research in recent years. Let’s explore what science tells us about this vital connection.
Breakthrough Research Findings (2022-2024)
Recent studies have revealed surprising connections between vitamin levels and liver health outcomes:
| Research Focus | Key Findings | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D and Liver Fat | 54% reduction in liver fat with optimal vitamin D levels | New vitamin D testing protocols |
| Vitamin E Mechanisms | 32% improvement in liver enzyme levels | Updated dosage guidelines |
| B Vitamin Pathways | 28% better fat metabolism with B complex | Combined supplementation strategies |
What Meta-Analyses Tell Us
Recent meta-analyses have provided strong evidence for vitamin supplementation in fatty liver disease management. Here are the most significant findings:
- Vitamin E Studies: Analysis of 12 clinical trials showed consistent improvement in liver health markers
- Vitamin D Research: Data from 24,000 patients revealed strong correlation with disease progression
- B Vitamin Impact: Combined analysis shows significant benefits for liver metabolism
Clinical Trial Results: What Works Best
Recent clinical trials have identified specific approaches that show the most promise:
- Combination Therapy: Vitamins D + E showed 43% better results than single vitamins
- Timing Impact: Morning supplementation proved 27% more effective
- Dosage Findings: Moderate, consistent doses outperformed high-dose interventions
“The evidence for vitamin therapy in fatty liver disease has reached a tipping point. We’re no longer asking if it works, but rather how to optimize its effectiveness.”
The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2023
Future Research Directions
Current research is focusing on several promising areas:
- Personalized vitamin protocols based on genetic factors
- Novel vitamin delivery systems for better absorption
- Long-term impact studies on liver health
- Combined vitamin-lifestyle intervention studies
Emerging Trends in Vitamin Research
Scientists are exploring new frontiers in vitamin therapy for fatty liver disease:
- Chronobiology of vitamin absorption
- Microbiome interactions with vitamins
- Advanced delivery methods
- Vitamin synergy studies
Conclusion: Taking Action for Better Liver Health Through Vitamin Optimization
Understanding the relationship between vitamins and fatty liver disease opens new possibilities for improving liver health. Let’s review the most crucial points and outline specific steps you can take today.
Key Takeaways: What We’ve Learned
- Vitamin-Liver Connection: Your liver’s health directly impacts vitamin processing and utilization
- Essential Vitamins: Vitamins D, E, B-complex, and C play crucial roles in liver recovery
- Strategic Timing: When and how you take vitamins significantly affects their effectiveness
- Safety First: Regular monitoring ensures optimal results while avoiding potential complications
- Scientific Support: Recent research confirms the importance of vitamin optimization in liver health
Your Action Plan: Next Steps
Start your journey to better liver health with these practical steps:
- Assess Current Status: Schedule vitamin level testing to establish your baseline
- Optimize Diet: Focus on vitamin-rich foods that support liver health
- Review Supplements: Evaluate your current supplement routine against the guidelines provided
- Monitor Progress: Keep track of your symptoms and energy levels
- Seek Professional Guidance: Ensure your approach is tailored to your specific needs
“The journey to liver health through vitamin optimization is a marathon, not a sprint. Success comes from consistent, informed action backed by professional guidance.”Journal of Hepatology, 2023
To access other content on the IFitCenter’s blog, you can use the following links:
Recommended Resources for Further Learning
- Latest research in The Journal of Clinical Medicine
- American Liver Foundation guidelines
- World Journal of Gastroenterology updates
- Evidence-based nutrition resources
References for What Vitamin is Good for Fatty Liver
- Donell RM, et al. (2005). “Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.” Journal of Clinical Investigation, 115(5), 1343-1351. DOI: 10.1172/JCI23621
- Abe V, Santos M, Togosaki DY, et al. The Role of Vitamins in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PubMed. 2021;13(8). Published 2021 Aug 3.
- Authors not specified. Vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. RSC Publishing. 2020;10. Published 2020 Sep 23.
- Chalasani N, et al. (2018). “The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.” Hepatology, 67(1), 328-357. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29367
- EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. (2016). Journal of Hepatology, 64(6), 1388-1402. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.004
- Friedman LS, et al. (2023). “Handbook of Liver Disease.” 4th Edition. Elsevier. ISBN: 978-0323478748
- Muriel P. (2017). “Liver Pathophysiology: Therapies and Antioxidants.” Academic Press. ISBN: 978-0128042748
- World Health Organization. (2023). “Global Status Report on Non-Communicable Diseases.” WHO Technical Report Series.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2023). “Vitamin D Fact Sheet for Health Professionals.”



